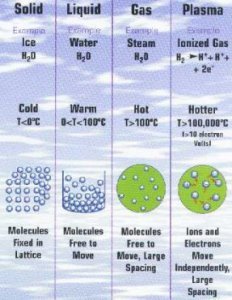
 Matter exists in three fundamental states (solid, liquid and gaseous), which depend on the temperature and pressure to which the matter is subjected.
Matter exists in three fundamental states (solid, liquid and gaseous), which depend on the temperature and pressure to which the matter is subjected.
amorphous solid
Body that resembles a congealed liquid whose atoms are not ordered.gas
Malleable and expandable matter whose only definable property is mass; its atoms are fully mobile with respect to each other.crystallization
Change of a substance from an amorphous state to a crystallized state; it results from cooling, which causes the atoms to become ordered.condensation
Change of a substance from a gaseous state to a liquid state; it results from cooling.evaporation
Change of a substance from a liquid state to a gaseous state; it results from heating.melting
Change of a substance from a solid state to a liquid state; it results from heating.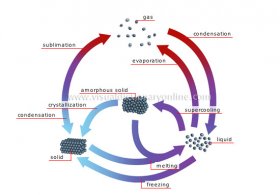
freezing
Change of a substance from a liquid state to a solid state; it results from cooling.sublimation
Change of a substance from a solid state directly to a gaseous state without passing through the liquid state; it results from heating.liquid
Matter having a definite mass and volume but no shape; its atoms are relatively mobile in relation to each other. Change of a substance from a gaseous state to a liquid state; it results from cooling.solid
Rigid body possessing mass, volume and a definite form; its atoms are linked to each other and are almost completely at rest.supercooling
The process of cooling a liquid below the point at which it normally freezes (solidifies); its atoms become unstable.YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE

Problems of Meaning in Science Curriculum (Ways of Knowing ...

The Meaning of Time In Science (1973) Educational Film

States of Matter-Science