 Continued coal use
Continued coal use
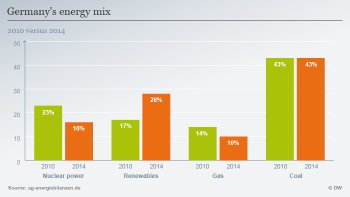
In the meantime, due in part to a sharp drop in prices for carbon emissions trading on the European market, production of electricity from coal has remained cost-competitive. Coal thus continues to be a major source of energy in Germany.
This despite Germany's carbon dioxide emission reduction goals, which consist of 40 percent reductions from 1990 levels by 2020. Experts have pointed out that continued use of coal-fired plants could prevent this goal from being reached.
"We will have to make additional efforts in this area, " Baake said. The government is thus seeking to reduce coal-based energy generation by introducing a levy on the most polluting brown-coal plants - which remains controversial.
'Energy battle'
German energy companies that for decades made billions off nuclear, gas and coal-fired electricity continue to seek public funding for transitioning their business models. They also face increasing competition from investment in renewables by citizens, farmers and companies.
Claudia Kemfert, of the German Institute for Economic Research in Berlin, described this as a "battle over energy." She said those who emphasize the high cost of renewables are attempting to discredit Germany's energy transition.
"It's not true - we have very low prices on the energy market, and if these were passed on to the consumer, the price of electricity would remain stable." She cited other reasons for the increase in electricity prices to Germans: about 12 percent over the last four years.
Nuclear waste: where, how much, who pays?
 Grafenrheinfeld: now still after 34 years of nuclear power production
Grafenrheinfeld: now still after 34 years of nuclear power production
Apart from continued debate over financing renewables, the phase-out of atomic energy in Germany comes with another major challenge: where to put nuclear waste so it can remain safely out of the environment for a million years.
The committee tasked with finding a final repository estimates that the process could take 30 to 80 years - potentially pushing the end of this process far into the next century.
Energy companies have set aside 36 billion euros ( billion) for the phase-out. According to a study by the German Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy, 22 billion euros have been planned for shutdown and dismantling of nuclear plants, and 17 billion for managing nuclear waste.
Yet the actual costs for this could run as high as 50 to 70 billion euros, warned Michael Müller, who heads the public committee for finding a final nuclear waste repository location. This represents a "substantial financial risk" for the German state and taxpayer, he added.
Atomic energy companies seek to pass along these costs to the state, while environmental groups are trying to block this. A number of disputes are wending their way through Germany's legal system, over interim nuclear waste repositories - as well as on claims by energy companies for lost profits from the immediate shutdown of nuclear plants after Fukushima.
Jürgen Resch of the German environmental organization Deutsche Umwelthilfe accused energy companies of "creeping out the back door" instead of facing financial responsibility.
The next nuclear scheduled to come offline is the B at Gundremmingen, by the end of 2017 at the latest. Representatives from industry have called for a "reliable roadmap" in provision of energy as further nuclear plants are shut down.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE