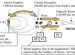
Atoms are made of three types of sub-atomic particle: neutrons and protons in the nucleus and electrons orbiting the nucleus.
Some materials are radioactive because the nucleus of each atom is unstable and gives out nuclear radiation in the form of alpha particles, beta particles or gamma rays. The radiation can be detected using a Geiger counter.
Nuclear reactors use a type of nuclear reaction called nuclear fission. Another type of nuclear reaction - nuclear fusion - happens in the Sun and other stars.

The structure of the atom
Atoms are made up of two main parts, the nucleus and orbiting electrons. Electrons can be lost or gained and this forms charged particles - ions.
The nucleus contains two types of particles called neutrons and protons. As protons, neutrons and electrons are the building blocks of atoms they're called sub-atomic particles.
Properties of sub-atomic particles
| Particle | Relative mass | Relative charge |
|---|---|---|
| Proton | +1 | |
| Neutron | ||
| Electron | Almost zero | -1 |
Some materials are radioactive because the nucleus of each atom is unstable and can decay, or split up, by giving out nuclear radiation in the form of alpha particles, beta particles or gamma rays. The nuclear radiation given off can be detected using a Geiger counter. The number of nuclei that decay and give off radiation every second is called the activity of the material and is measured in becquerel A unit of radioactivity (Bq)..
Example
If a radioactive material has an activity of 200 Bq, in 1 second 200 of its nuclei will decay and give off radiation. In 1 minute 12, 000 (= 200 x 60) nuclei will decay.
The activity of a radioactive material will decrease with time. This will be shown by a falling count rate, measured using the Geiger counter.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE